We have the largest International Internet Gateway (IIG) service providers in Bangladesh which is connected to the International Internet Traffic through BSCCL (SMW4, SMW5), BTTB, Tata Communications Limited, Bharti Airtel Limited, Singapore Telecommunications Limited, COGENT, NTT, HURRICANE and TIS. We also have IX connectivity over international IPLC services with Equinix and SGIX in Singapore and Mumbai-IX in India. This platform has increased customer experience and greater reachability geographically. By using our distinguished International networks our clients have International IP coverage and convergence services throughout North America, Europe and Asia-Pacific. While having the widest PoP presence in cities and all over the country, along with integrated network with global partners, our networks are fully redundant with almost 99.99% uptime. SComm has already built rld class (1+1) infrastructure systems and services for the customers under IIG network. bsccl_tender_document_example.pdf
SMW4: The SMW4 submarine cable system connects 14 landing stations across 17 countries. The cable has a design capacity of 1.28 Tbps and provides high-speed connectivity between South East Asia, the Middle East, and Western Europe.
SMW5: The SMW5 submarine cable system connects 16 landing stations across 20 countries. The cable has a design capacity of 24 Tbps and provides high-speed connectivity between South East Asia, the Middle East, and Western Europe.
TIS The Thailand - Indonesia - Singapore Cable Network (TIS) is a 1100-km regional submarine network linking Songkhla (Thailand), Batam (Indonesia) and Changi (Singapore). The TIS consortium includes CAT Telecom Public Company Ltd. of Thailand (CAT), PT Telekomunikasi Indonesia Tbk of Indonesia (Telin) and Singapore Telecommunications Limited of Singapore (SingTel) which jointly invested 36 million to build the TIS cable network.
The I-ME-WE (India-Middle East-Western Europe) submarine cable system is a high-speed telecommunications network that connects India, This cable system also provides connectivity to multiple countries in the Middle East and Europe, but not directly to Bangladesh.
Example SComm IPT COGENT
Landing Points: The cable has landing points in the following countries:
- India: Mumbai and Chennai
- Pakistan: Karachi
- United Arab Emirates: Fujairah
- Saudi Arabia: Jeddah
- Egypt: Alexandria
- Italy: Catania
- France: Marseille
- Spain: Marseilles and Barcelona
IP Transit
Summit Communications Limited is providing IP Transit network services for middle and large sized clients. It is a suitable service for Internet Service Providers, with a public AS (Autonomous System) number and the hardware and competence to handle dynamic BGP routing.
IP Transit, short for Internet Protocol Transit, refers to the service of providing internet connectivity between a customer's network and the rest of the internet, while PNI ( Private Network Interconnect) is a direct interconnection between two networks to exchange internet traffic.
Default route vs full routing table:
A default route is a special route that is used when there is no specific route in the routing table for a particular destination. It is often denoted as “0.0.0.0/0” and is typically used as a fallback option. In contrast, a full routing table contains all the available routes for a given network, including specific routes for individual subnets.
In terms of size, a default route is much smaller than a full routing table because it only includes one route. However, a default route can be less efficient than a full routing table in terms of routing traffic because it may send traffic through unnecessary network hops. A full routing table provides more specific routing information and can be more efficient in terms of routing traffic, but it also requires more memory and processing power to maintain.
Partial route: A partial Internet route refers to a subset of routes that are used to reach a specific destination on the internet.
- <DHPALAGGR-02>display route-policy DOT-INT-OUT
- Route-policy: DOT-INT-OUT
- deny : 10 (matched counts: 0)
- Match clauses:
- if-match community-filter BLACKHOLE
- permit : 20 (matched counts: 0)
- Match clauses:
- if-match as-path-filter DOT-INT-OUT
- deny : 30 (matched counts: 0)
- <DHPALAGGR-02>display current-configuration | in DOT-INT-OUT
- Info: It will take a long time if the content you search is too much or the string you input is too long, you can press CTRL_C to break.
- peer 103.15.245.234 route-policy DOT-INT-OUT export
- route-policy DOT-INT-OUT deny node 10
- route-policy DOT-INT-OUT permit node 20
- if-match as-path-filter DOT-INT-OUT
- route-policy DOT-INT-OUT deny node 30
- ip as-path-filter DOT-INT-OUT index 10 permit ^[0-9]+$
To receive the full routing table on your router, you will need to do the following:
- Ensure that your router has enough memory and processing power to handle the full routing table. The exact requirements will depend on the size of the routing table and the capabilities of your router.
- Configure your router to establish BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) peering sessions with one or more upstream routers or peers that can provide you with the full routing table. This will typically involve configuring BGP parameters such as autonomous system (AS) numbers, IP addresses, and authentication settings.
- Ensure that your router has the necessary routing policies and filters in place to handle the incoming routes. This may include configuring prefix-lists, route-maps, and other BGP policies to control which routes are accepted and how they are processed.
- Monitor your router's performance and resource utilization to ensure that it is able to handle the full routing table effectively. This may involve adjusting BGP parameters, scaling up hardware resources, or optimizing routing policies as needed.
The global full routing table contained over 910000 active routes. However, this number is constantly changing as new routes are added and old ones are removed.
In some cases, a default route or a partial routing table may be sufficient for routing traffic to the desired destinations. It's important to carefully evaluate the routing requirements and capabilities of your network before attempting to receive the full routing table.
IIG TO IX Multilateral peering
Multilateral peering is a type of peering arrangement in which multiple internet service providers (ISPs) exchange traffic with each other through a single point of interconnection, typically a neutral internet exchange point (IXP). In this arrangement, each ISP establishes a peering relationship with the IXP, and through that relationship, they can exchange traffic with all other ISPs connected to the IXP.
Bilateral peering:
It is a type of peering arrangement between two Internet Service Providers In a bilateral peering arrangement, two ISPs establish a direct connection between their networks at the IXP, and agree to exchange traffic based on a mutually agreed-upon peering policy.
The advantages of bilateral peering include: Improved network performance: Bilateral peering reduces network latency and improves network performance by providing a direct path for traffic between the two networks.
Lower costs: Bilateral peering can reduce the costs associated with transit providers, as it allows the two ISPs to exchange traffic directly without having to pay for transit.
Increased control: Bilateral peering gives ISPs more control over their network traffic, as they can prioritize certain types of traffic or route traffic in specific ways.
Bilateral peering active policy:
- Restrictive ( TATA )
- Selective ( Priority network )
- Open peering ( google & fcebook )
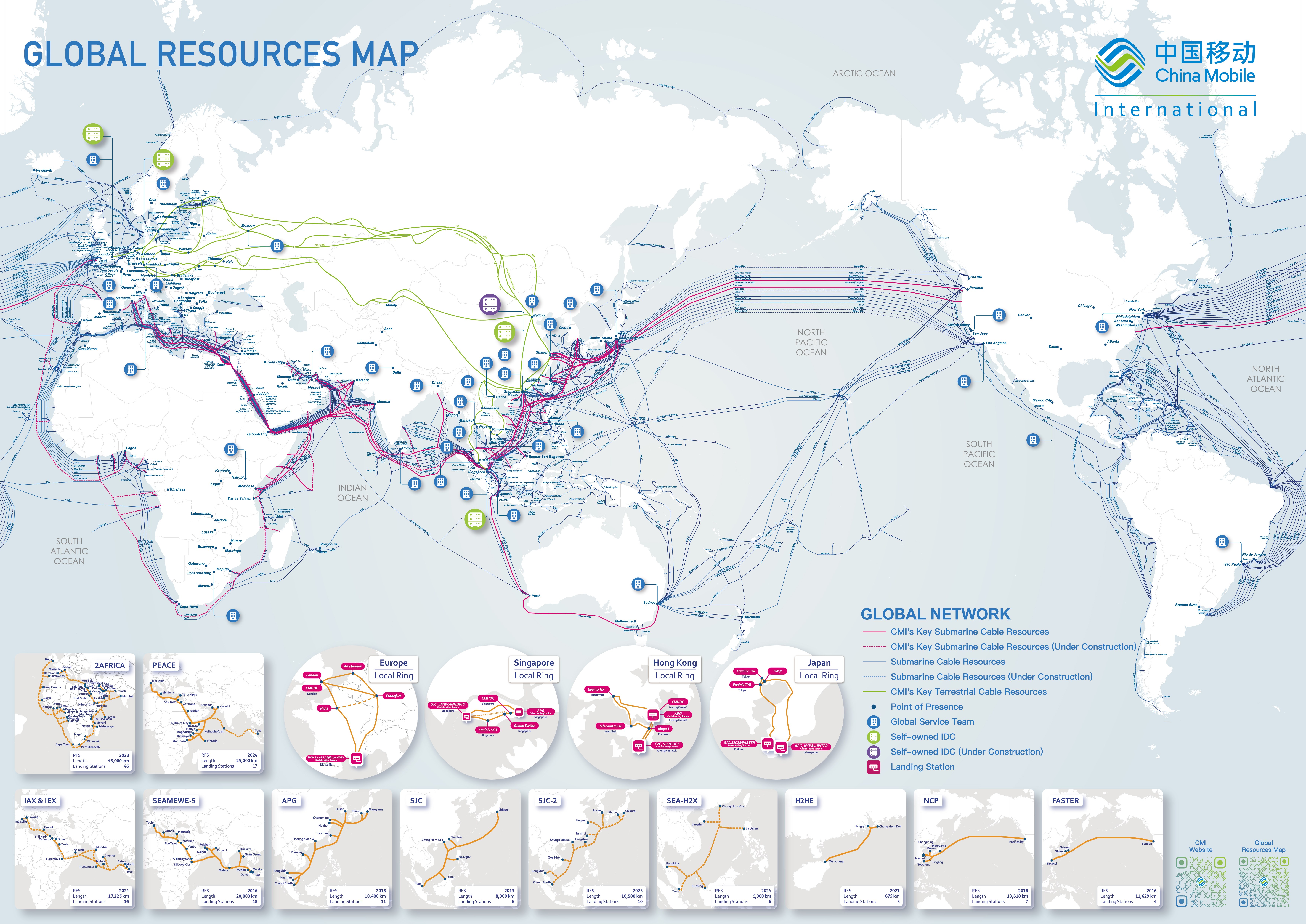
Submarine Cable Map
LOOKING GLASS AND WHOIS URL
IP blacklist check and reputation lookup tools:
Colocation DC example Scomm singapore singtel ? The term colocation refers to several aspects of this type of data center. First, the term references the fact that servers and other equipment from many different companies are ‘co-located’ in one data center. The hardware is usually ow
https://www.racksolutions.com/news/data-center-trends/what-is-a-colocation-data-center/